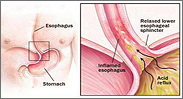
GERD
GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) is a common condition involving the esophagus (the muscular tube that connects the back of the mouth ot the stomach) that can occur at any age, but typically begins to appear around age 40. many people refer to this disorder as heartburn or indigestion, GERD is caused when the muscular valve at the lower end of the esophagus relaxes, allowing the contents of the stomach to backwash, or reflux, into the esophagus. These gastric contents contain strong acids and bile that are very irritating to the lining of the esophagus.
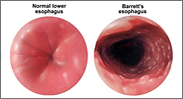
BARRETT’S ESOPHAGUS
The esophagus is the muscular tube that carries food and saliva from the mouth to the stomach. Barrett’s esophagus is a condition resulting from ongoing irritation of the esophagus where its normal lining is replaced by the type of lining that is normally found in the stomach. Patients with the Barrett’s esophagus lack symptoms that noticeably different from gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), the underlying irritation in most cases.
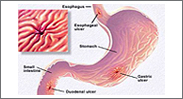
PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE
Peptic ulcers happen when the acids that help you digest food damage the walls of the stomach orduodenum. The most common cause is infection with a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori. Another cause is the long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) such as aspirin and ibuprofen. Stress and spicy foods do not cause ulcers but can make them worse.
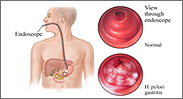
HELICOBACTOR PYLORI (H.PYLORI)
This bacterium infect the lining of the stomach and thrives in the mucous environment. It is common worldwide and especially impacts the elderly, the very young, and those in Third World countries where sanitation is problematic. However, just because you have been exposed to H.pylori doesn’t necessarily mean you will be affected by its presence. Often H.pylori does not cause any symptoms . Approximately 50 percent of people in the United States have it.
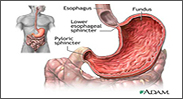
GASTRITIS
Gastritis describes a group of conditions with one thing in common: inflammation of the lining of the stomach. The inflammation of gastritis is often the result of infection with the same bacterium that causes most stomach ulcers. However, other factors — such as injury, regular use of certain pain relievers or drinking too much alcohol — also can contribute to gastritis. In some cases, gastritis can lead to ulcers and an increased risk of stomach cancer. For most people, however, gastritis isn’t serious and improves quickly with treatment.
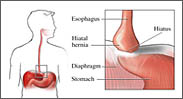
HIATAL HERNIA
A hiatal hernia occurs when part of your stomach pushes upward through your diaphragm. Your diaphragm normally has a small opening (hiatus) through which your food tube (esophagus) passes on its way to connect to your stomach. The stomach can push up through this opening and cause a hiatal hernia.In most cases, a small hiatal hernia doesn’t cause problems, but a large hiatal hernia can allow food and acid to back up into your esophagus, leading to heartburn. very large hiatal hernia sometimes requires surgery.
NAUSEA AND VOMITING
Nausea is an uneasy or unsettled feeling in the stomach together with an urge to vomit. Nausea and vomiting, are not diseases. They can be symptoms of many different conditions. These include morning sickness during pregnancy, infections, migraine headaches, motion sickness, food poisoning, or other medicines. For vomiting in children and adults, avoid solid foods until vomiting has stopped for at leastsix hours. Then work back to a normal diet. Drink small amounts of clear liquids to avoid dehydration.
GASTROPARERSIS
Gastroparesis literally translated means “stomach paralysis”. Is a digestive disorder in which the motility of the stomach is either abnormal or absent. When the stomach is functioning normally, contractions of the stomach help to crush ingested food and then propel the pulverized food into the small intestine where further digestion and absorption of nutrients occurs. When gastroparesis is present the stomach is unableto contract normally, and therefore cannot crush food nor propel food into the small intestine properly.
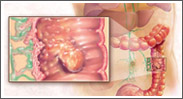
GASTROINTESTINAL CANCERS
Refers to malignant conditions of the gastrointestinal tract, these are: esophagus, stomach, biliary system pancreas, and anus. Stomach cancer can develop in any part of the stomach and can spread throughout the stomach and to other organs such as the smallintestines, lymph nodes, liver pancreas and colon. Hepatocellular carcinoma is a cancer that arises in the liver. It is also known as hepatoma or primary liver cancer. The risk of cancer of the esophagus is also increased by irritation of the lining of the esophagus.
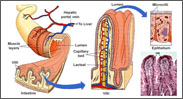
CELIAC SPRUE
Celiac sprue is a chronic disease of the digestive tract that interferes with the digestion and absorption of nutrients from food. People with celiac sprue cannot tolerate gluten, a protein commonly found in wheat, rye, barley and oats. When affected individuals ingest foods containing gluten, the lining (mucosa) of the intestine becomes damaged due to the body’s immune reaction.
